20 Sep2019
By Renee Rybak Lang

The AACTE Programs and Professional Learning team served on the committee to select the following inaugural Civic Engagement Champions with the National Association of State Boards of Education and the Frank Islam Institute.
Four middle school teachers have been named Civic Engagement Champions (CEC) for their work in promoting civics education and active citizenship.
In partnership with the Frank Islam Institute for 21st Century Citizenship (FII), the National Association of State Boards of Education (NASBE) created the CEC award to highlight the critical role that middle school teachers play in helping students become active, responsible citizens. Teachers from four states representing each of NASBE’s regions—Illinois, Massachusetts, Maryland, and Washington—were eligible to apply.
The four winners are Jane Leyderman, Dever Elementary School in Chicago, IL; Michael Neagle, Pyne Arts Magnet School in Lowell, MA; Michelle St. Pierre, Loch Raven Technical Academy in Baltimore County, MD; and Don Jenkins, North Whidbey Middle School in Oak Harbor, WA.
18 Sep2019
By Danny Ryan

The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development’s (OECD) work on education helps individuals and nations to identify and develop the knowledge and skills that drive better jobs and better lives, generate prosperity, and promote social inclusion.
Access to OECD Education data
Through the OECD data portal, educators can cross-reference data on teacher’s salaries, graduation rates, education spending, and much more. All data is available to download for free.
For example, are you curious about how education policies support students, teachers, and principals? The OECD’s new Education Policy Outlook reports on the progress of over 200 school improvement policies implemented over the last 10 years.
School and University leaders will find a treasure trove of information within the OECD Teaching and Learning International Survey (TALIS), which asks teachers and school leaders about working conditions and learning environments at their schools to help countries face diverse challenges.
For those wanting further OECD insight, the OECD iLibrary contains nearly 20,000 content items related to education. Content on the platform is accessible to all by clicking the READ or WEB icon. Certain features and access is restricted to intuitions that have a subscription. Find out if your institution is an existing subscriber.
12 Sep2019
By Middle Tennessee State University and SCORE
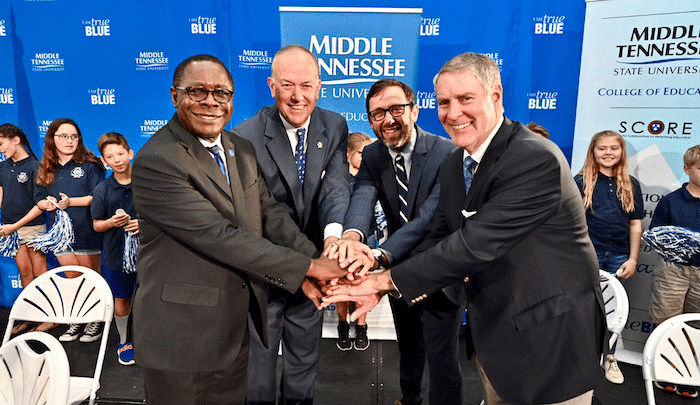
This article and photo originally appeared on the Middle Tennessee State University website and are reprinted with permission.
Middle Tennessee State University announced Wednesday (Aug. 28) a first-of-its-kind partnership focused on bringing research-supported innovations to how the university prepares students to become K-12 teachers.
09 Sep2019
By Joanne Van Boxtel and Heather Taylor Wizikowski

This article and photo originally were originally published in SmartBrief Education and are reprinted with permission.
We all know the numbers are sobering. A 2018 brief from the Council for Exceptional Children showed critical shortages of special education teachers in 48 states and the District of Columbia. Fifty-one percent of all school districts and 90% of high-poverty school districts report difficulty recruiting highly qualified special education teachers. The exit rate for special education teachers is nearly twice that of general education teachers and enrollment in teacher training programs has declined by 35% over the previous five years.
It seems a dismal picture, but there is light at the end of the tunnel — one that prepares teachers to enter this dynamic field and equips them with tools to help them skillfully and confidently persist in the profession.
29 Aug2019
By Genesis Gonzalez
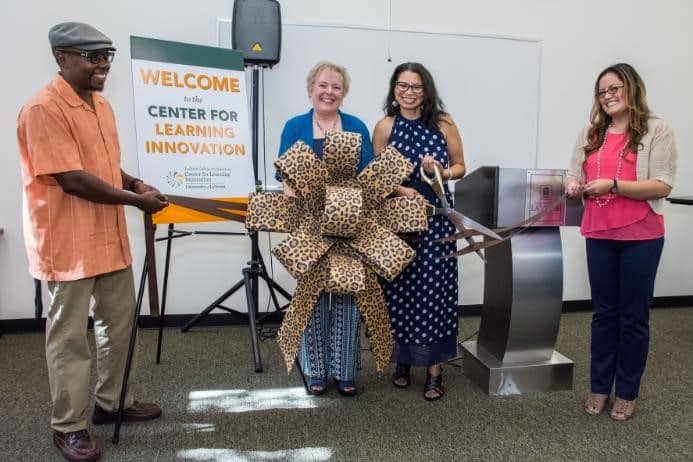

This article and photo originally appeared on the University of La Verne website and are reprinted with permission.
The University of La Verne’s LaFetra College of Education welcomes the new Center for Teacher Leadership & Learning Innovation, a first-of-its-kind lab, designed to support and train educators from across Los Angeles County and the Inland Empire in 21st-century learning competencies.
“As a College of Education, which prepares community and school leaders, support providers and teachers, it is imperative that our faculty be
22 Aug2019
By Emily Stembridge
 The IMPACT-PD grant—Improving Preschoolers’ Acquisition of Language through Coaching Teachers and Professional Development—is playing an integral role in providing preschool educators the tools they need to help their students develop proficiency in English as a second language.
The IMPACT-PD grant—Improving Preschoolers’ Acquisition of Language through Coaching Teachers and Professional Development—is playing an integral role in providing preschool educators the tools they need to help their students develop proficiency in English as a second language.
The United States Department of Education National Professional grant, funded by the Office of English Language Acquisition, aims to provide educators with professional development opportunities for improving instruction of dual-language learners in preschool.
The IMPACT-PD program, a partnership between the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the Alabama Department of Early Childhood Education, focuses on four goals to further training and education to children learning English early in life:
16 Aug2019
By Kate Robertson
This article originally appeared in on the University of Tulsa Appalachian website and is reprinted with permission.
Oklahoma is facing a troubling teacher shortage. To ensure public school students have instructors in classrooms this fall, the state has issued 3,000 emergency teacher certifications. The Oklahoma Association of Colleges for Teacher Education (OACTE) analyzed data to uncover the ramifications of an increased number of emergency certificates, and on Monday, Aug. 12, The University of Tulsa hosted the Oklahoma Teacher Pipeline Summit to share their findings and discuss possible solutions to the crisis.
14 Aug2019
By Jacqueline Rodriguez
 As the student population has diversified so has our understanding of the general education classroom, specifically who we serve in an inclusive setting. Our students with special education services are learning the majority of their grade level curriculum in general education classrooms. This paradigm shift requires effective collaboration between service providers and teachers as well as a deep understanding and application of differentiation to meet the needs of all students.
As the student population has diversified so has our understanding of the general education classroom, specifically who we serve in an inclusive setting. Our students with special education services are learning the majority of their grade level curriculum in general education classrooms. This paradigm shift requires effective collaboration between service providers and teachers as well as a deep understanding and application of differentiation to meet the needs of all students.
For years, the two fields of general education and special education have been siloed. Persistence and partnership is how
13 Aug2019
By Katrina Norfleet

The September/October 2019 issue of the Journal of Teacher Education (JTE) is now available online, while printed copies are arriving in the mail to subscribers around the country. Below is a summary of the articles included in Vol. 70, Issue 4, 2019:
In “Teacher Agency and Resilience in the Age of Neoliberalism,” members of the JTE editorial team, Tonya Bartell, Christine Cho, Corey Drake, Emery Petchauer, and Gail Richmond, address how the articles in this issue provide insights into ways educator preparation programs can support teachers in developing and enacting agency. They discuss how making small shifts or adaptations in everyday teaching practices can create more just and equitable teaching and learning.
In the paper, “Whiteness as a Dissonant State: Exploring One White Male Student Teacher’s Experiences in Urban Contexts,” Stephanie Behm Cross of Georgia State University, Nermin Tosmur-Bayazit of Fitchburg State University, and Alyssa Hadley Dunn of Michigan State University, suggest that Whiteness itself is a dissonant state. The authors argue that
09 Aug2019
By Jacqueline Rodriguez
 The key to developing the Bowling Green State University (BGSU) dual licensure program is reaching out to the local area to ensure the program is built with the local needs at the forefront. “The local data is how the university can drive change,” recalls a district leader. Faculty also believe collaboration with the district is central to their mission and their success with candidates. Making connections with the field office and the supervising teachers ensured faculty could relate what candidates were seeing in the field to what they were learning in their coursework.
The key to developing the Bowling Green State University (BGSU) dual licensure program is reaching out to the local area to ensure the program is built with the local needs at the forefront. “The local data is how the university can drive change,” recalls a district leader. Faculty also believe collaboration with the district is central to their mission and their success with candidates. Making connections with the field office and the supervising teachers ensured faculty could relate what candidates were seeing in the field to what they were learning in their coursework.
University systems must also be taken into consideration, especially when working across colleges and across departments. Two questions drove the BGSU program leadership as they developed their dual licensure program: What is best for our students in this program? An what is best for this program? One significant concern was finding strong clinical placements for each teacher candidate. The success of a program with hundreds of teacher candidates rested with strong clinical partnerships.
Finally, serving all students that walk into the classroom was the priority when developing the dual licensure program at BGSU. “This wasn’t an experiment, this is the way BGSU does business,” reflected a faculty member. It was a choice to move away from single licensure that, over time, changes the makeup of the district teaching population, which is why district leaders were involved at every step in the program development.
To learn more, watch the Advice to Others video highlighting BGSU’s Models of Inclusive Clinical Teacher Preparation, part of AACTE’s Research-to-Practice Spotlight Series.
09 Aug2019
By Lindsay Tuman
This article originally appeared on Fox 8 News and is reprinted with permission.
The Guilford County School District is getting more teachers with the help of a new program.
Guilford County Schools, High Point University and North Carolina A & T State University partnered together for the Teacher Quality Partnership. It’s a federal grant that helps get highly qualified teachers into high-needs schools.
The grant awards more than $4 million to get 25 participants into an accelerated program. In this program, they will learn what they need to be an effective teacher while applying the skills simultaneously in their own classroom with the help of a mentor.
“I never thought I would be in the classroom. People have been telling me for years, ‘Oh, you’d be a great teacher,’” Rashida Queen, one of the
01 Aug2019
By Jacqueline Rodriguez
 A number of students in Portland State University’s (PSU) Secondary Dual Education Program (SPED) recently reflected on advice they were given before entering the graduate program. “I always want more education than less,” one teacher candidate was advised by a mentor in the field of medicine. The candidate now looks back on her experience in the program with appreciation. “I was ready. I had the resources. I had been in the classroom for two years; it felt natural. I didn’t have the same level of trepidation as some of my first year friends.”
A number of students in Portland State University’s (PSU) Secondary Dual Education Program (SPED) recently reflected on advice they were given before entering the graduate program. “I always want more education than less,” one teacher candidate was advised by a mentor in the field of medicine. The candidate now looks back on her experience in the program with appreciation. “I was ready. I had the resources. I had been in the classroom for two years; it felt natural. I didn’t have the same level of trepidation as some of my first year friends.”
The students who complete the PSU program graduate with a dual endorsement in a secondary education content area and special education. Another candidate reflected on the importance of serving every student in the classroom. His decision to pursue a two-year graduate program in secondary English and special education was an obvious one; it ensured he would be prepared to meet the needs of all students with a range of abilities.
The benefit of being profession-ready is not only valued by the teacher candidates. High school students also note the tremendous advantage they have when a teacher who understands the unique needs of students with IEPs is leading the classroom. In particular, college access traditionally has been stymied for students with significant disabilities. However, one high school student reflected that she has a mentor in her teacher, someone who has guided her toward college-ready curriculum. Learning from their students is another area of mutual benefit expressed by the candidates. The necessity to meet the needs of each student in the classroom is universally acknowledged by candidates, students, and administrators.
To learn more, view the What’s in it for me? video highlighting PSU’s Secondary Dual Education program, part of AACTE’s Research-to-Practice Spotlight Series.
31 Jul2019
By Diane Angelucci
 This article originally appeared in Rowan Today and is reprinted with permission.
This article originally appeared in Rowan Today and is reprinted with permission.
Even in the best school districts, obstacles to equal education and opportunities can hide far below the surface
To help districts unearth and address these issues, the Center for Access, Success and Equity (CASE) in Rowan University’s College of Education has forged equity-focused research practice partnerships with several school districts—one of CASE’s three research areas. CASE is establishing research as central to the College of Education in three ways — through partnerships with districts, through grant-funded research, and through the College’s Ph.D. program.
“I can’t speak enough about our experience with CASE,” said Piera Gravenor, superintendent of Delsea Regional School District, which has worked with CASE for the last two years.
31 Jul2019
By Charles Tocci, Terri Pigott and Ann Marie Ryan
 Untold amounts of time and money are invested in making changes to teaching practice, often with the best intentions and limited ideas about how to actually pull it off. In early May, the Woodrow Wilson Foundation announced a major new initiative to change the way American history is taught across the country. The Foundation argues that it is a failure of teaching that two out of three Americans cannot pass the U.S. citizenship exam. Accordingly, its new “American History Initiative” will include an online platform for professional development, lessons, and interactive learning materials as well as expanded teacher fellowships and research on curriculum. It is a sizable, much needed, and laudable investment of resources in history education. However, one key question remains: Why do they think this will work?
Untold amounts of time and money are invested in making changes to teaching practice, often with the best intentions and limited ideas about how to actually pull it off. In early May, the Woodrow Wilson Foundation announced a major new initiative to change the way American history is taught across the country. The Foundation argues that it is a failure of teaching that two out of three Americans cannot pass the U.S. citizenship exam. Accordingly, its new “American History Initiative” will include an online platform for professional development, lessons, and interactive learning materials as well as expanded teacher fellowships and research on curriculum. It is a sizable, much needed, and laudable investment of resources in history education. However, one key question remains: Why do they think this will work?
29 Jul2019
By Jerrica Thurman
 Developing and sustaining partnerships with local school districts are critical to the success of the Bowling Green State University (BGSU) Inclusive Early Childhood (IEC) program. Superintendents who work with BGSU assert that all parties need to understand the challenges each school district and university face and must be willing to bridge the gap between research and clinical practice together. BGSU’s teacher candidates are deployed for clinical practice in special education at local schools including in rural areas.
Developing and sustaining partnerships with local school districts are critical to the success of the Bowling Green State University (BGSU) Inclusive Early Childhood (IEC) program. Superintendents who work with BGSU assert that all parties need to understand the challenges each school district and university face and must be willing to bridge the gap between research and clinical practice together. BGSU’s teacher candidates are deployed for clinical practice in special education at local schools including in rural areas.
“One of the pieces that works really well for us is that all of the people working in the education department at the university are parents themselves of students in our district so there’s a vested interest,” said Francis Scruci, superintendent of Bowling Green City Schools. “I think there’s a mutual respect. We certainly respect what the university does and I think they respect what we’re trying to do at the K-12 level and we understand the challenges that both of us face. We are willing to bridge that gap and try to help each other become successful.”
BGSU’s overall objective is to prepare graduates of the IEC program to teach young children with and without disabilities in inclusive settings. The IEC program blends the best practices from early childhood education with early childhood special education. It addresses the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to meet the needs of each child. Graduates of the program are prepared to provide differentiated, evidence-based instruction to young children from birth through grade 3.
To learn more, watch the Developing and Sustaining Partnerships video highlighting BGSU’s Models of Inclusive Clinical Teacher Preparation, part of AACTE’s Research-to-Practice Spotlight Series.












 The IMPACT-PD grant—Improving Preschoolers’ Acquisition of Language through Coaching Teachers and Professional Development—is playing an integral role in providing preschool educators the tools they need to help their students develop proficiency in English as a second language.
The IMPACT-PD grant—Improving Preschoolers’ Acquisition of Language through Coaching Teachers and Professional Development—is playing an integral role in providing preschool educators the tools they need to help their students develop proficiency in English as a second language. As the student population has diversified so has our understanding of the general education classroom, specifically who we serve in an inclusive setting. Our students with special education services are learning the majority of their grade level curriculum in general education classrooms. This paradigm shift requires effective collaboration between service providers and teachers as well as a deep understanding and application of differentiation to meet the needs of all students.
As the student population has diversified so has our understanding of the general education classroom, specifically who we serve in an inclusive setting. Our students with special education services are learning the majority of their grade level curriculum in general education classrooms. This paradigm shift requires effective collaboration between service providers and teachers as well as a deep understanding and application of differentiation to meet the needs of all students.
 The key to developing the Bowling Green State University (BGSU) dual licensure program is reaching out to the local area to ensure the program is built with the local needs at the forefront. “The local data is how the university can drive change,” recalls a district leader. Faculty also believe collaboration with the district is central to their mission and their success with candidates. Making connections with the field office and the supervising teachers ensured faculty could relate what candidates were seeing in the field to what they were learning in their coursework.
The key to developing the Bowling Green State University (BGSU) dual licensure program is reaching out to the local area to ensure the program is built with the local needs at the forefront. “The local data is how the university can drive change,” recalls a district leader. Faculty also believe collaboration with the district is central to their mission and their success with candidates. Making connections with the field office and the supervising teachers ensured faculty could relate what candidates were seeing in the field to what they were learning in their coursework.
 This article originally appeared in
This article originally appeared in  Untold amounts of time and money are invested in making changes to teaching practice, often with the best intentions and limited ideas about how to actually pull it off. In early May, the
Untold amounts of time and money are invested in making changes to teaching practice, often with the best intentions and limited ideas about how to actually pull it off. In early May, the